arrow_back_ios
Main Menu
arrow_back_ios
Main Menu
- Mechanical & structural DAQ systems
- Sound & Vibration DAQ systems
- Industrial electronics
- Simulator Systems
- Electric power analyzers
- S&V Handheld devices
- Wireless DAQ Systems
- DAQ
- Drivers API
- nCode - Durability and Fatigue Analysis
- ReliaSoft - Reliability Analysis and Management
- Test Data Management
- Utility
- Vibration Control
- Inertial Sensor Software
- Test Data Management
- Asset Monitoring
- Sensor Finder
- Acoustic
- Current / voltage
- Displacement
- Exciters
- Force
- Inertial Sensors
- Load cells
- Multi Component
- Pressure
- Smart Sensors with IO-Link interface
- Strain
- Fiber Optic Temperature Sensors
- Fiber Optic Tilt Sensors
- Torque
- Vibration
- OEM Custom Sensors
- Calibration Services for Transducers
- Calibration Services for Handheld Instruments
- Calibration Services for Instruments & DAQ
- On-Site Calibration
- Resources
- Articles
- Case Studies
- Recorded Webinars
- Primers and Handbooks
- Videos
- Whitepapers
- Search all resources
- Acoustics
- Data Acquisition & Analysis
- Durability & Fatigue
- Electric Power Testing
- Industrial Process Automation
- Machine automation control and navigation
- NVH
- Reliability
- Smart Sensors
- Structural Health Monitoring
- Vibration
- Virtual Testing
- Weighing
- Road Load Data Acquisition
arrow_back_ios
Main Menu
- QuantumX
- SomatXR
- MGCplus
- Optical Interrogators
- CANHEAD
- eDAQ
- Strain Gauge precision instrument
- Bridge calibration units
- GenHS
- LAN-XI
- Fusion-LN
- CCLD (IEPE) signal conditioner
- Charge signal conditioner
- Microphone signal conditioner
- NEXUS
- Microphone calibration system
- Vibration transducer calibration system
- Sound level meter calibration system
- Accessories for signal conditioner
- Accessories for calibration systems
- Multi channel amplifier
- Single channel amplifier and amplifier with display
- Weighing indicators
- Weighing electronics
- Accessories for industrial electronics
- eDrive power analyzer
- eDrive Package - Remote Probe based
- eGrid power analyzer
- GenHS
- Accessories for power analyzer and GenHS
- BK Connect / PULSE
- Tescia
- Catman data acquisition software
- Thousands of Channels at a Glance
- Perception – High speed data acquisition software
- Drivers for compatibility with third party software
- ReliaSoft BlockSim
- ReliaSoft Cloud
- ReliaSoft Lambda Predict
- ReliaSoft MPC
- ReliaSoft Product Suites
- ReliaSoft RCM++
- ReliaSoft XFMEA
- ReliaSoft XFRACAS
- ReliaSoft Weibull++
- Classical Shock
- Random
- Random-On-Random
- Shock Response Spectrum Synthesis
- Sine-On-Random
- Time Waveform Replication
- Vibration Control Software
- Microphone sets
- Cartridges
- Reference microphones
- Special microphones
- Acoustic material testing kits
- Acoustic calibrators
- Hydrophones
- Microphone Pre-amplifiers
- Sound Sources
- Accessories for acoustic transducers
- Fiber Optic Technology
- Inductive technology
- Strain gauge technology
- Accessories for displacement sensors
- Inertial Measurement Units (IMU)
- Vertical Reference Units (VRU)
- Attitude and Heading Reference Systems (AHRS)
- Inertial Navigation Systems (INS)
- Inertial Sensor Accessories
- Bending / beam
- Canister
- Compression
- Single Point
- Tension
- Weighing modules
- Digital load cells
- Accessories for load cells
- Strain gauges for experimental testing
- Fiber optical strain gauges
- Strain gauges for transducer manufacturing (OEM)
- Strain sensors
- Accessories for strain gauges
- Accelerometers
- Force transducers
- Impulse hammers / impedance heads
- Tachometer probes
- Vibration calibrators
- Cables
- Accessories
- Force - OEM custom sensors
- Torque - OEM custom sensors
- Load - OEM custom sensors
- Multi-Axis - OEM custom Sensors
- Pressure - OEM custom sensors
- HATS (Head and torso simulator)
- Artificial Ear
- Electroacoustic hardware
- Bone conduction
- Electroacoustic software
- Pinnae
- Accessories for electroacoustic application
- Accessories
- Actuators
- Combustion Engines
- Durability
- eDrive
- Mobile Systems
- Production Testing Sensors
- Transmission Gearboxes
- Turbo Charger
- Force Calibration
- Torque Calibration
- Microphones & Preamplifiers Calibration
- Accelerometers Calibration
- Pressure Calibration
- Displacement Sensor Calibration
- Sound Level Meter Calibration
- Sound Calibrator & Pistonphone Calibration
- Vibration Meter Calibration
- Vibration Calibrator Calibration
- Noise Dosimeter Calibration
- QuantumX Calibration
- Genesis HighSpeed Calibration
- Somat Calibration
- Industrial Electronics Calibration
- LAN-XI Calibration
- Guidelines on Calibration Intervals
- Certificate Samples
- Interactive Calibration Certificate
- Download of Calibration Certificates
- Acoustics and Vibration
- Asset & Process Monitoring
- Data Acquisiton
- Electric Power Testing
- Fatigue and Durability Analysis
- Mechanical Test
- Reliability
- Weighing
- Electroacoustics
- Noise Source Identification
- Handheld S&V measurements
- Sound Power and Sound Pressure
- Noise Certification
- Acoustic Material Testing
- Structural Durability and Fatigue Testing
- Durability Simulation & Analysis
- Material Fatigue Characterisation
- Electrical Devices Testing
- Electrical Systems Testing
- Grid Testing
- High-Voltage Testing
- End of Line Durability Testing
- Vibration Testing with Electrodynamic Shakers
- Structural Dynamics
- Machine Analysis and Diagnostics
- Troubleshooting Analyser
- Naval Certification and Sea-Trials
- Process Weighing
- Sorting and Batching Solutions
- Scale Manufacturing Solutions
- Vehicle Scale Solutions
- Filling, Dosing and Checkweighing Control
arrow_back_ios
Main Menu
- Housing
- Communication processor
- Amplifier modules
- Connection boards
- Special function modules
- Accessories for MGCplus
- Binaural Audio
- Outdoor microphones
- Probe Microphones
- Sound intensity probes
- Surface microphone
- Array microphones
- Other special microphones
- Microphones for production line test
- Probe microphones
- Microphone Cables
- Tripods
- Microphone booms
- Microphone adapters
- Electrostatic actuators
- Microphone windscreen
- Nose cones
- Microphone holders
- Other accessories for acoustic transducers
- Microphones outdoor protection
- Rod end bearings
- Tensile load introductions
- Thrust pieces and load buttons
- Cables and connectors
- Screw sets
- Load bases / Tensile compressive adapters
- Measurement cables
- Ground cables
- Thrust pieces
- Bearings
- Load feet
- Base plates
- Knuckle eyes
- Adapters
- Mounting aids and others
- Adhesives
- Protective coatings
- Cleaning material
- SG Kits
- Solder terminals
- Other strain gauge accessories
- Cables
- ZeroPoint Balancing
- TCS Balancing
- TC0 Balancing
- Magnets
- Mounting clips/bases
- Studs, screws and washers
- Adhesives/Tools
- Adapters
- Mechanical filters
- Other accessories
- High-Force LDS Shakers
- Medium-Force LDS Shakers
- Low-Force LDS Shakers
- Permanent Magnet Shakers
- Shaker Equipment / Slip Tables
- Testing Of Hands-Free Devices
- Smart Speaker Testing
- Speaker Testing
- Hearing Aid Testing
- Headphone Testing
- Soundbar Testing
- Telephone Headset And Handset Testing
- Acoustic Holography
- Acoustic Signature Management
- Underwater Acoustic Ranging
- Wind Tunnel Acoustic Testing – Aerospace
- Wind Tunnel Testing For Cars
- Beamforming
- Flyover Noise Source Identification
- Real-Time Noise Source Identification With Acoustic Camera
- Sound Intensity Mapping
- Spherical Beamforming
- Product Noise
- HighVoltage HighPower Switchgear Tests
- Transformer Testing
- Current Zero Testing
- Circuit Breaker Testing
- Messung der Unrundheit von Eisenbahnrädern
- On-Board Measurement
- Pantograph and Overhead Lines Monitoring
- Wayside Train Monitoring & Measurement
- Shock and Drop Testing
- Environmental Stress Screening - ESS
- Package Testing
- Buzz, Squeak and Rattle (BSR)
- Mechanical Satellite Qualification - Shaker Testing



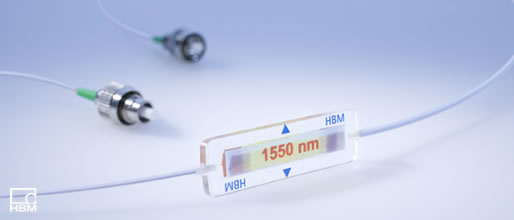
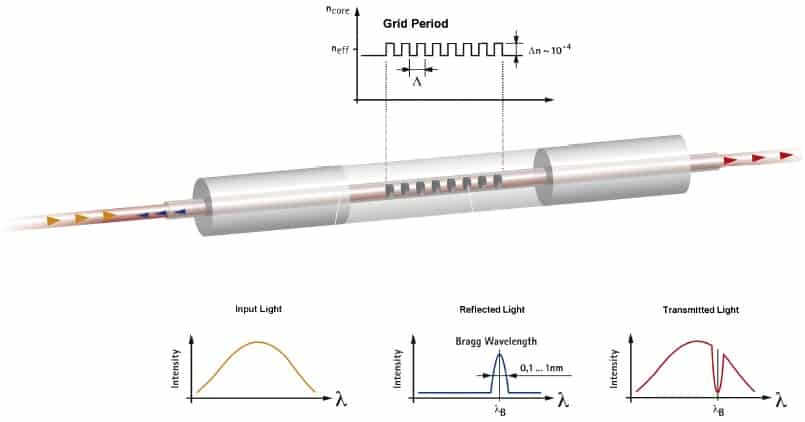 Bragg grating sensors consist of an optical fiber that contains a distributed Bragg reflector. The most frequently-used technology involves inscribing nano-structured Bragg gratings in the form of periodic variations of the optical refractive index into the core of the optical fibers, as shown in Figure 1.
The length of the Bragg grating is approximately 4 – 6 mm. The Bragg grating acts like a filter, reflecting a particular wavelength of light and transmitting all others.
The dimensions of the grating determine the light frequency that it reflects. The reflected wavelength (λB), called the Bragg wavelength, is defined by the equation, λB = 2n · Λ where n is the effective refractive index of the grating in the fiber core and Λ is the grating period. As the sensor is compressed or stretched, n and Λ change and the value of λB changes.
Bragg grating sensors consist of an optical fiber that contains a distributed Bragg reflector. The most frequently-used technology involves inscribing nano-structured Bragg gratings in the form of periodic variations of the optical refractive index into the core of the optical fibers, as shown in Figure 1.
The length of the Bragg grating is approximately 4 – 6 mm. The Bragg grating acts like a filter, reflecting a particular wavelength of light and transmitting all others.
The dimensions of the grating determine the light frequency that it reflects. The reflected wavelength (λB), called the Bragg wavelength, is defined by the equation, λB = 2n · Λ where n is the effective refractive index of the grating in the fiber core and Λ is the grating period. As the sensor is compressed or stretched, n and Λ change and the value of λB changes.
 An energy company recently installed an HBM measurement system using fiber optic sensors to monitor a section of gas pipeline in Germany. Because the pipeline runs through a river valley, regulations called for the pipeline to be monitored 24 hours a day, seven days a week. The system monitors local stresses, ensuring pipeline integrity even if there is some movement caused by geological activity.
The fiber optic sensors are installed on the pipeline as shown in Figure 2. When installed in this way, the system monitors several crucial pipeline parameters, including how far the pipeline actually moves and the rate of change of the movement.
For this particular application, there are eight HBM Optimet fiber optic sensor chains with six sensors in each chain. Each sensor in the chain operates at a slightly different frequency in the 1,500 – 1,600 nm band. Because of this, the entire chain can be connected to a data acquisition system with only two fiber optic cables. One supplies the light source, while the second provides the input signal to the interrogator.
An energy company recently installed an HBM measurement system using fiber optic sensors to monitor a section of gas pipeline in Germany. Because the pipeline runs through a river valley, regulations called for the pipeline to be monitored 24 hours a day, seven days a week. The system monitors local stresses, ensuring pipeline integrity even if there is some movement caused by geological activity.
The fiber optic sensors are installed on the pipeline as shown in Figure 2. When installed in this way, the system monitors several crucial pipeline parameters, including how far the pipeline actually moves and the rate of change of the movement.
For this particular application, there are eight HBM Optimet fiber optic sensor chains with six sensors in each chain. Each sensor in the chain operates at a slightly different frequency in the 1,500 – 1,600 nm band. Because of this, the entire chain can be connected to a data acquisition system with only two fiber optic cables. One supplies the light source, while the second provides the input signal to the interrogator.
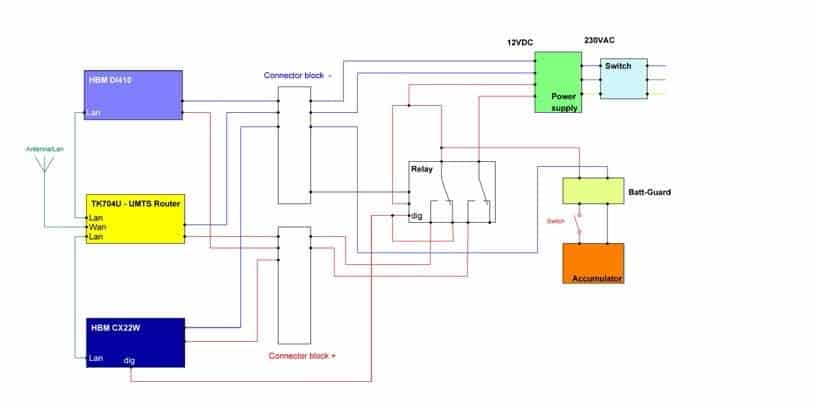 The system, as shown in Figure 3 consists of:
The system, as shown in Figure 3 consists of:






