arrow_back_ios
See All 软件 See All 仪表 See All 传感器 See All 振动测试设备 See All 电声 See All 声学生产下线检测系统 See All 应用 See All 行业 See All 服务 See All 支持 See All 全球业务 Main Menu
arrow_back_ios
See All 可靠性 See All 数据采集软件 See All 驱动程序和API See All 公用程序 See All 振动控制 See All 高精度和校准系统 See All 数据采集系统 See All 手持式声级和振动测量 See All 工业仪表 See All 功率分析仪 See All 信号适调器 See All 声学传感器 See All 电流和电压传感器 See All 位移传感器 See All 力传感器 | 测力传感器 See All 称重传感器 See All 多分量传感器 See All 压力传感器 See All 应变传感器 See All 应变片 See All 温度传感器 See All 倾角传感器 See All 扭矩传感器 See All 振动传感器 See All 振动控制器 See All 测量激振器 See All 模态激振器 See All 功率放大器 See All LDS振动台系统 See All 振动测试设备附件 See All 测试解决方案 See All 执行器 See All 内燃机 See All 耐用性 See All 电驱动 See All 生产测试传感器 See All 变速器和齿轮箱 See All 涡轮增压器 See All 声学 See All 基础结构和过程监控 See All 电功率 See All 数据采集与分析 See All 耐久性和疲劳 See All NVH See All OEM定制传感器 See All 振动 See All 结构完整性 See All 称重 See All 汽车和地面运输 See All 校准 See All 现场安装、维护和修理 See All Brüel & Kjær 技术支持 Main Menu
arrow_back_ios
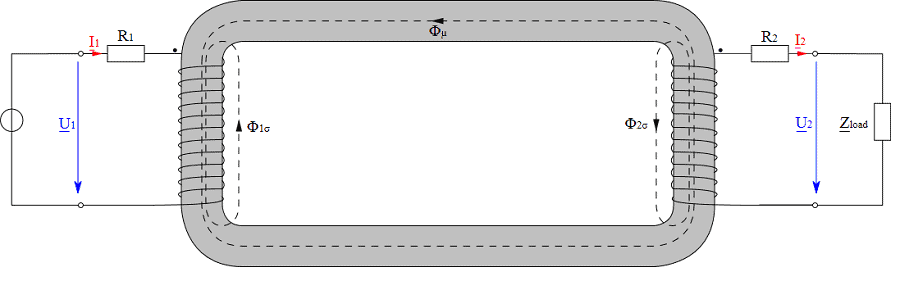
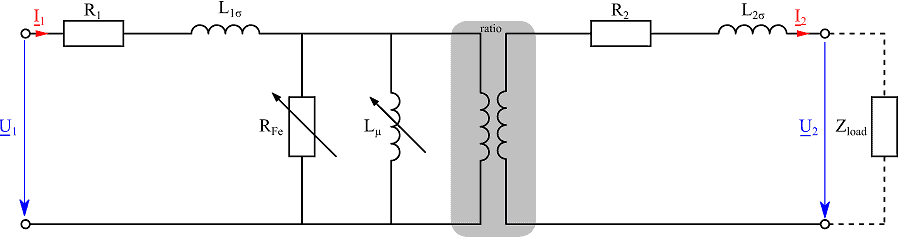
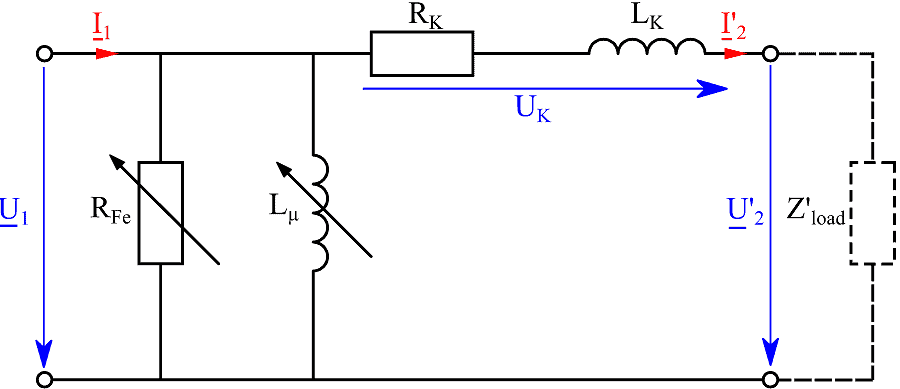
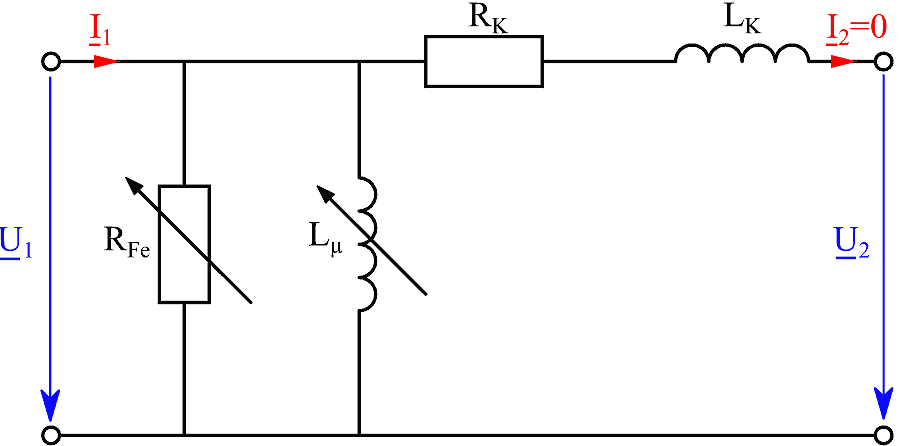
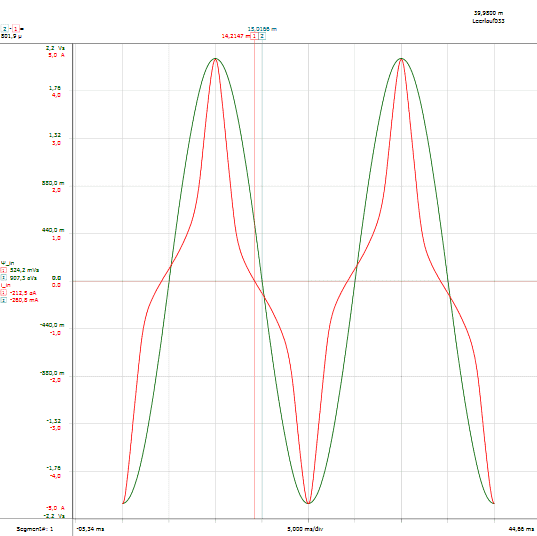
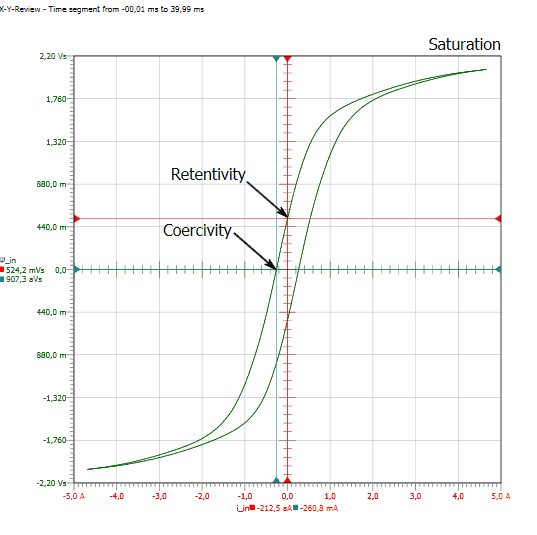
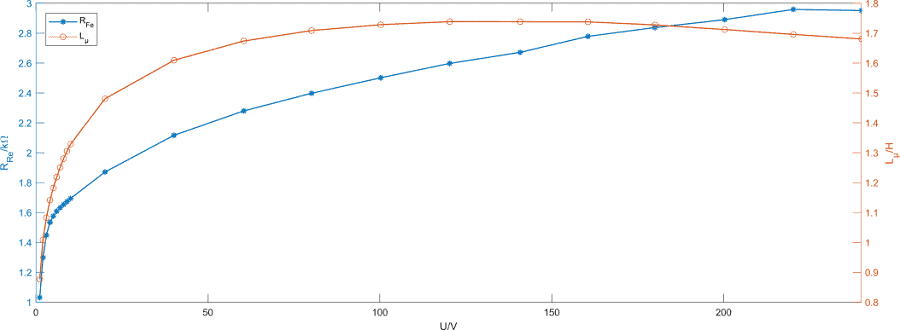
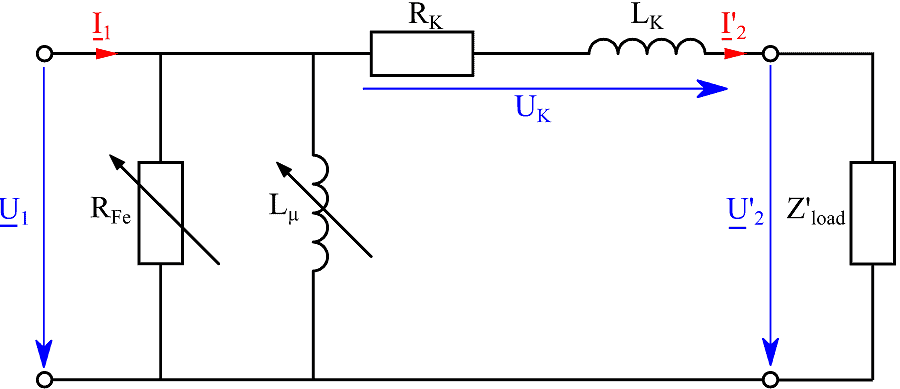
See All API See All 电声 See All 噪声源识别 See All 环境噪声 See All 声功率和声压 See All 噪声认证 See All 结构健康监测 See All 工业过程控制 See All 电池测试 See All 瞬时测量电力的介绍 See All 变压器等效电路图 | HBM See All 农业行业的OEM传感器 See All 用于机器人和扭矩应用的OEM传感器 See All 结构动力学 See All 机械分析和诊断 See All 结构动力学 See All 材料性能测试 See All 过程称重 See All 传感器校准服务 See All 手持设备校准 See All 仪表和DAQ 校准 See All 资源 See All 软件许可管理